Introduction
Music therapy (MT) is gaining traction as a non-pharmacological means to support cognitive and behavioral health in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This systematic review (PMCID: PMC10041788) analyzes how MT affects key domains such as global cognition, memory, language, processing speed, verbal fluency, and attention in AD patients.choosingtherapy.com+10pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+10nchr.elsevierpure.com+10
🧪 Methods
- Search scope: PubMed, Cochrane Library, HINARI (Jan 2012–Jun 2022)
- Inclusion: Randomized controlled trials comparing MT vs. standard care or non-musical interventions
- Studies included: 8 RCTs, 689 participants aged ~60–87 years
- Locations: Europe (France, Spain), Asia (China, Japan), USA
- Quality: 6 of 8 trials rated high qualityresearchgate.net+3pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+3ouci.dntb.gov.ua+3ouci.dntb.gov.ua
📊 Key Findings
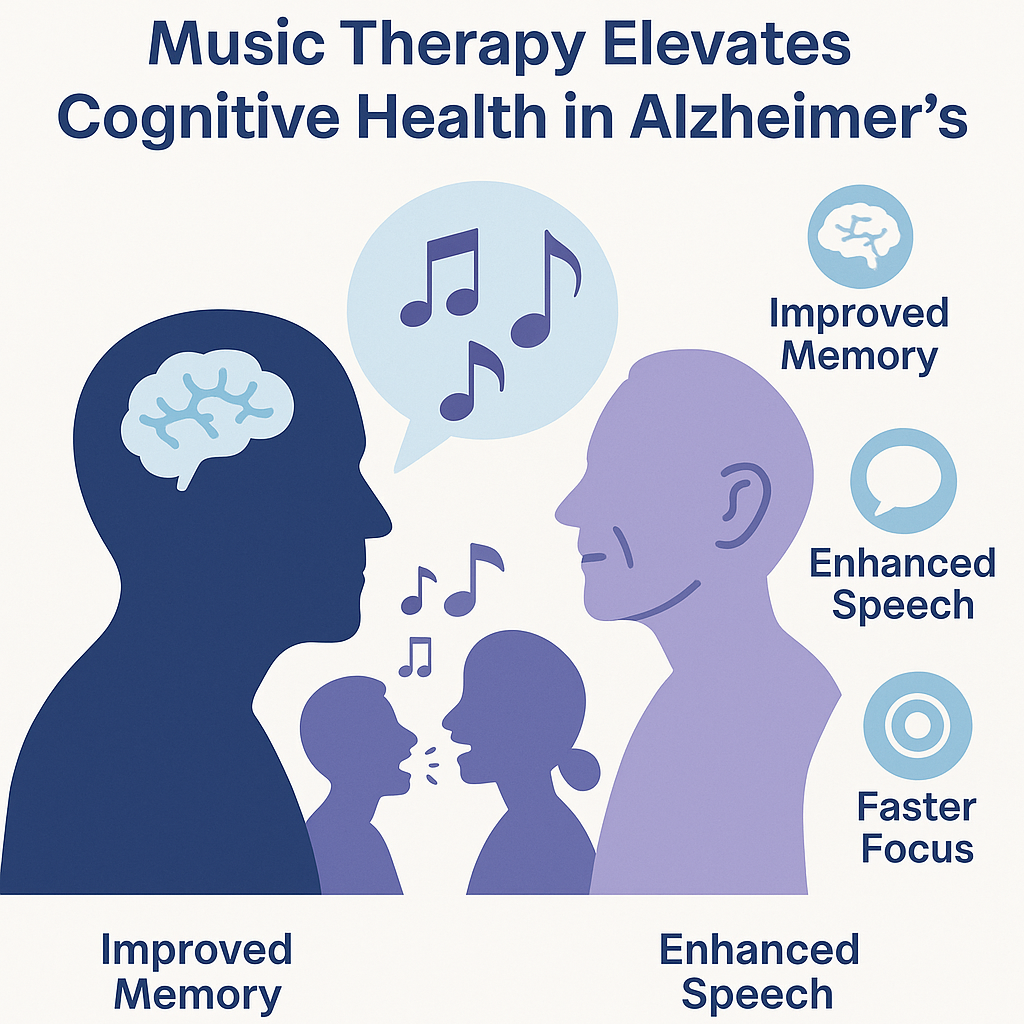
- Global Cognitive Function
- MT led to overall improvement in cognitive scores compared to controlsresearchgate.net+4pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+4mdpi.com+4.
- Memory & Verbal Fluency
- Enhanced memory retention and language skills were observed, often linked to individualized musicplaylists and active participation en.wikipedia.org+9pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+9ouci.dntb.gov.ua+9.
- Attention & Processing Speed
- Participants showed better focus and quicker cognitive responses during and after MT sessionshealthline.com+14pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+14alzres.biomedcentral.com+14.
- Impact of Active Music Interventions (AMI)
- AMI—where patients engage in singing, clapping, or playing—was notably more effective than passive listening en.wikipedia.org+9pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+9researchgate.net+9.
- Music Type Matters
- Familiar or classical tunes (e.g., Bach, Mozart) enhanced cognitive response, supporting personalized, preference-based MT artofit.org.
🧭 Conclusions & Implications
- MT demonstrates promise as a supportive therapy for improving cognition in AD—without adverse effectshealthline.com+5pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+5nchr.elsevierpure.com+5.
- Best results come from active, patient-tailored interventions.
- However, the limited number (8) of studies and variability in MT protocols necessitate larger, standardized trials with long-term follow-up healthline.com+4pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+4nchr.elsevierpure.com+4.
🎯 Practical Takeaways
- Clinicians & caregivers may incorporate music therapy as a complementary method for memory, speech, and attention enhancement in AD.
- Individualized music based on the patient’s history increases engagement and cognitive benefit.
- Future studies should aim to clarify the most effective formats, session durations, and music genres for diverse AD populations.